Technical insight into potential functional-related characteristics (FRCs) of sodium starch glycolate, croscarmellose sodium and crospovidone
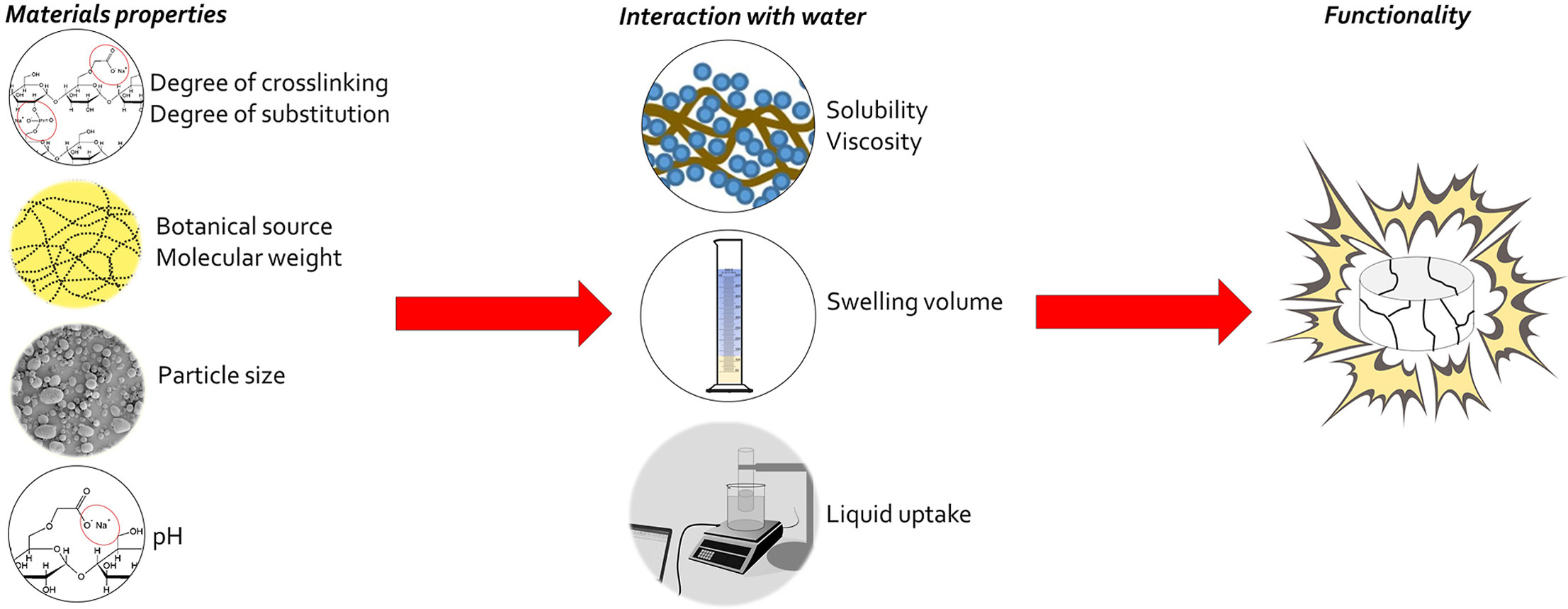
Functional-related characteristics (FRCs) are properties of excipients that can potentially influence one or more functions of that excipient in the final product. Knowledge of FRCs is important for formulation development and also to assess the risks of excipient variability on final product quality. Superdisintegrants are complex excipients, which main function is that to drive tablets disintegration. Although potential FRCs of superdisintegrants are listed in the Pharmacopeias and covered by some studies in the literature, a coherent understanding of the relation between FRCs themselves and with product functionality is still elusive.
This review aims at summarizing and link the scattered information available on superdisintegrants FRCs, focusing on sodium starch glycolate, croscarmellose sodium and crospovidone. After an analysis of the chemical structure of the three superdisintegrants, the influence of FRCs on functionality and stability of the final product is discussed. The FRCs that are addressed in this review are: physico-chemical material properties (material source, degree of crosslinking, degree substitution, pH, molecular weight, particle size, viscosity, water soluble substances, settling volume, liquid uptake) and reactive impurities.
In the conclusion of the review, we envision how the development of final products of high quality and consistency can be supported by simultaneously i) improving the understanding of FRCs of superdisintegrants, and ii) sharing of actual data on FRCs between excipient manufacturers and pharmaceutical dosage form manufacturers. Finally, we also foresee how knowledge of FRCs could drive upcoming innovation in superdisintegrants products’ development.
Continue reading here
About this article: Alberto Berardi, Pauline H.M. Janssen, Bastiaan H.J. Dickhoff, Technical insight into potential functional-related characteristics (FRCs) of sodium starch glycolate, croscarmellose sodium and crospovidone, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, Volume 70, 2022, 103261, ISSN 1773-2247, ttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103261. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S177322472200171X)

