Formulation development of loratadine immediate-release tablets using hot-melt extrusion and 3D printing technology
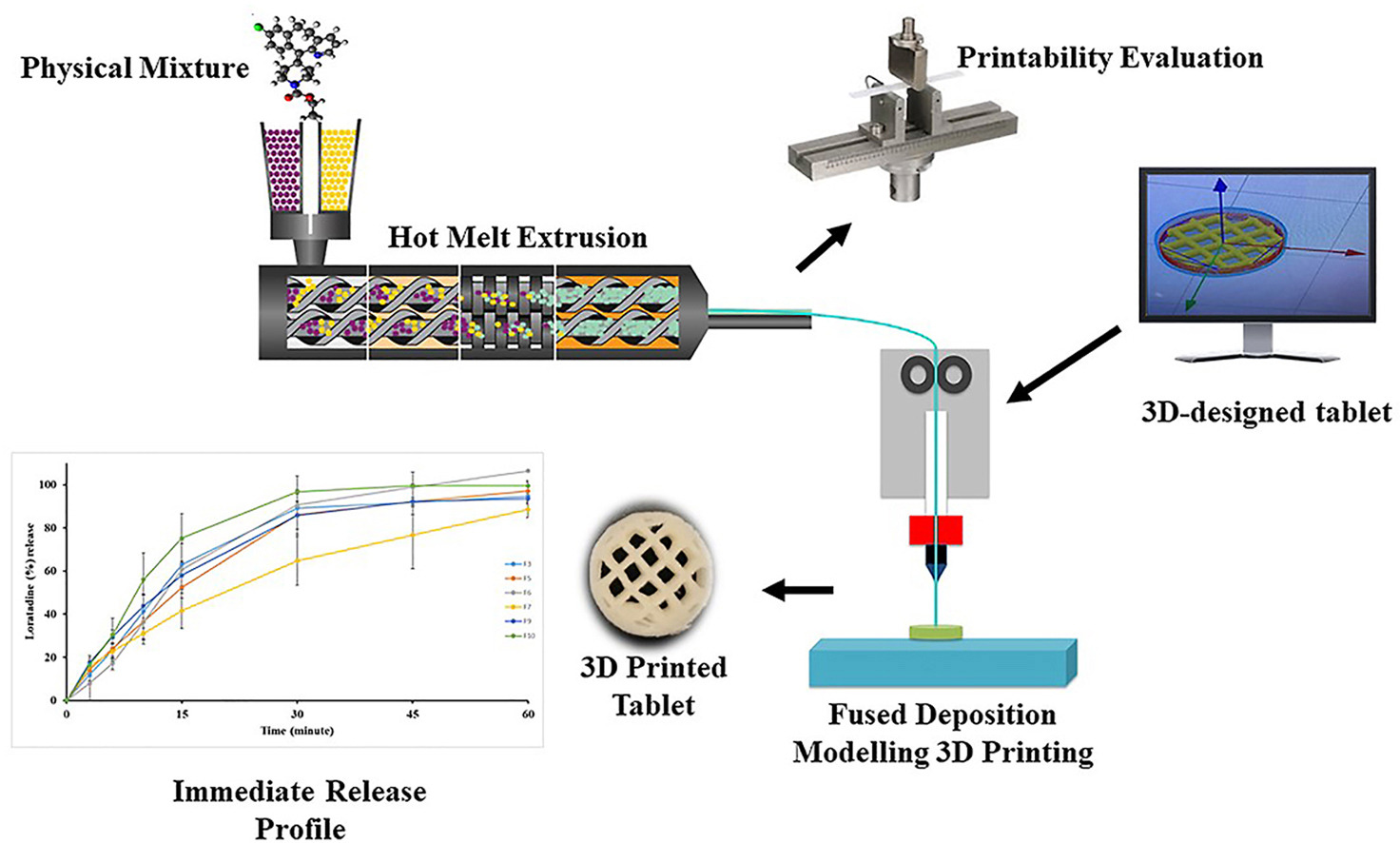
The main goal of this study was to develop immediate release Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printed loratadine tablets using hot-melt extrusion (HME) filaments. Loratadine was used as a model drug with 10% (w/w) drug loading. Ten different formulations were prepared using Crospovidone and croscarmellose as super-disintegrants, mannitol as a pore-forming agent, and polyethylene oxide-N80 and hydroxypropyl cellulose-EF as polymeric carriers. A three-point bend test was performed to determine the filaments’ elasticity, strength, and stiffness in order to evaluate the filaments printability.
The printable filaments were then printed using an (Prusa i3 MK3S) FDM-3D printer in a grid pattern and with (40–60%) infill to accelerate the drug release. The physical mixtures, filaments, and 3D printed tablets were analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was performed to investigate the interactions between loratadine and polymeric carriers. The in-vitro drug release profile of the printed tablets was tested. Based on the filament’s mechanical properties, six filaments were printable. The DSC thermograms indicated complete solubilization of loratadine in the polymeric carrier. All printed tablets exhibited a drug release of (86.1–96.9%) in 30 minutes. HME showed great potential to develop immediate release filaments which were suitable for FDM-3D printing.
Sundus Omari, Eman A. Ashour, Rasha Elkanayati, Mohammed Alyahya, Mashan Almutairi, Michael A. Repka,
Formulation development of loratadine immediate- release tablets using hot-melt extrusion and 3D printing technology,
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2022, 103505, ISSN 1773-2247,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103505.

