Formulation and Evaluation of Olmesartan Medoxomil Tablets
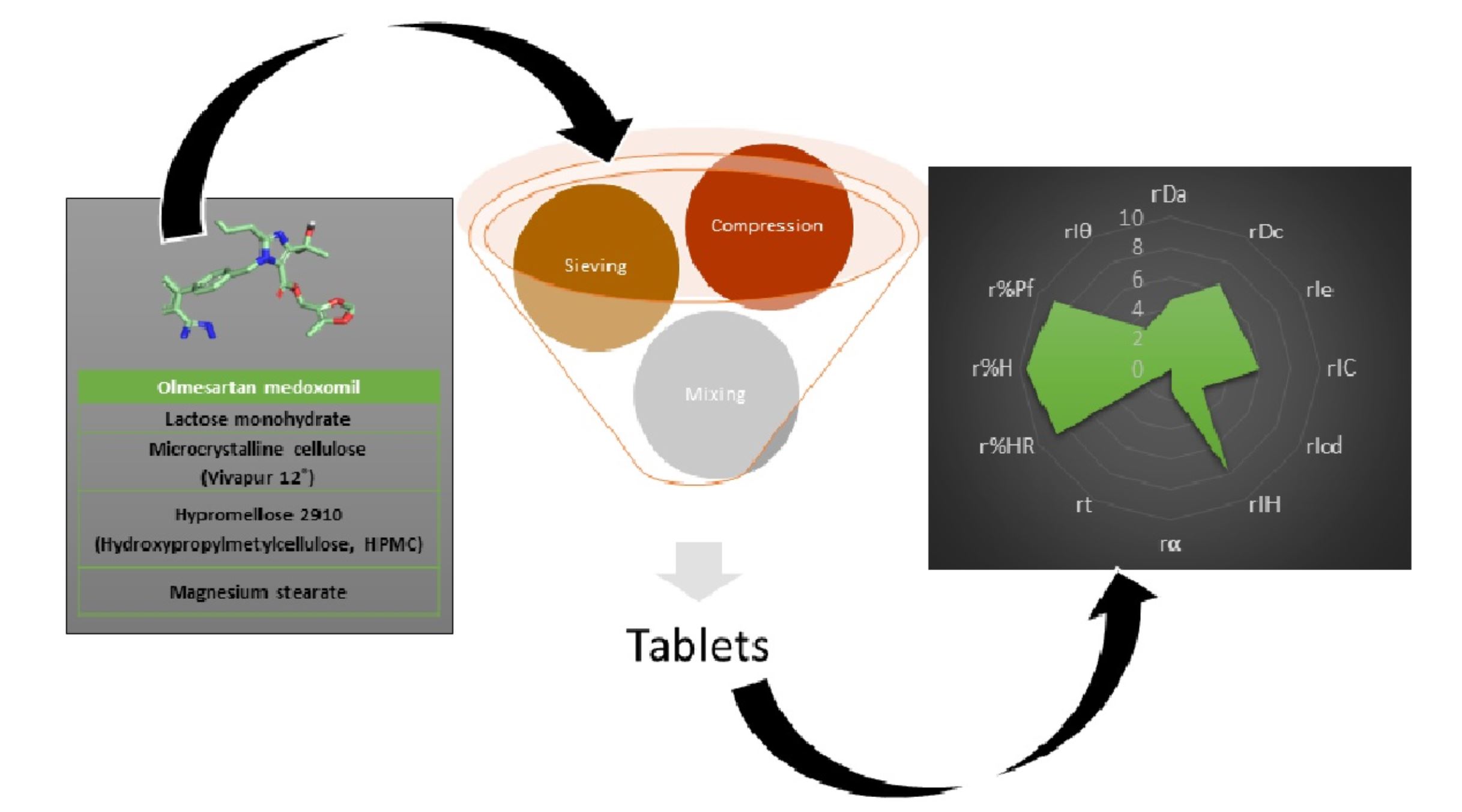
This work proposes a methodology for the design, development, and characterization of tablets prepared by the direct compression method of olmesartan medoxomil. The main objective was to ensure a high dissolution rate of the active ingredient. Therefore, a rigorous selection of excipients was carried out to ensure their physical and chemical compatibility with the active ingredient by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) studies. The suitability of the mixture for use in direct compression was performed using SeDeM methodology. The tablets met pharmacopoeia specifications for content uniformity, breaking strength, friability, and disintegration time.
Introduction
Finally, a spectrophotometric analytical method was developed to identify from the correct mixing in the production process to the concentration of olmesartan medoxomil in the tablets.
Download the full article as PDF here Formulation and Evaluation of Olmesartan Medoxomil Tablets
or read it here
Materials
Olmesartan medoxomil (Insud Pharma, Madrid, Spain) (Figure 1), lactose monohydrate (Guinama, Valencia, Spain), microcrystalline cellulose (Vivapur 12®, JRS Pharma GmbH & CO.KG, Berlin, Germany), hypromellose (HPMC 2910), JRS Pharma GmbH & CO.KG, Berlin, Germany) and magnesium stearate (Guinama, Valencia, Spain).
González, R.; Peña, M.Á.; Torrado, G. Formulation and Evaluation of Olmesartan Medoxomil Tablets. Compounds 2022, 2, 334-352. https://doi.org/10.3390/compounds2040028

