Development and implementation of a pneumatic micro-feeder for poorly-flowing solid pharmaceutical materials
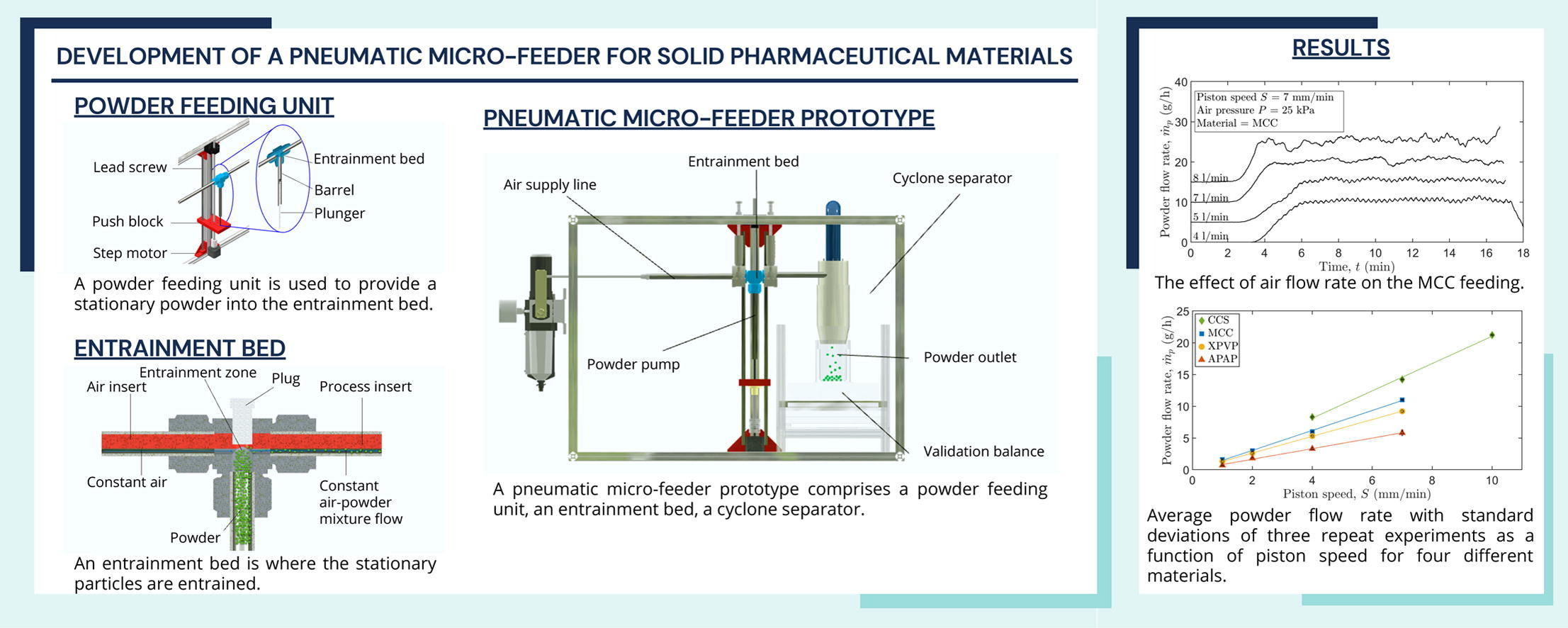
Consistent powder micro-feeding (< 100 g/h) is a significant challenge in manufacturing solid oral dosage forms. The low dose feeding can well control the content consistency of the dosage forms, which improves drug efficiency and reduces manufacturing waste. Current commercial micro-feeders are limited in their ability to feed < 20 g/h of cohesive (i.e. powders of poor flowability) active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and excipients (e.g. lubricants) with low fluctuation. To breach this gap, this study presents an advanced micro-feeder design capable of feeding a range of pharmaceutical-grade powders consistently at flow rates as low as 0.7 g/h with less than 20% flow rate variation. This was possible due to a novel powder conveying concept utilising particle re-entrainment to minimise flow rate variations.
This work details the design of this pneumatic micro-feeder and its excellent micro-feeding performance even for cohesive powders. The experimental studies investigated the influence of the process parameters (air pressure and air flow rate) and equipment configurations (insert size and plug position) on the feeding performance of different pharmaceutical relevant powders, i.e., microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), croscarmellose sodium (CCS), crospovidone (XPVP) and paracetamol (APAP). It was shown that the system is capable of delivering consistent powder flow rates with good repeatability and stability.
Dowload the full article as PDF here Development and implementation of a pneumatic micro-feeder for poorly-flowing solid pharmaceutical materials
or read it here
Materials
Four powders with a wide range of properties were used to assess the performance of the feeder design: microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) (VIVAPUR 112 from JRS pharma, Germany), croscarmellose sodium (CCS) (JRS pharma, Germany), crospovidone (XPVP) (Kollidon® CL, BASF), and an active pharmaceutical ingredient, paracetamol (APAP) (Ph Eur Powder from Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, Ireland). The selected MCC is a common material used as a filler in typical tablet formulations. It is selected to understand this system’s powder behaviour and optimise the system. Croscarmellose sodium and crospovidone are common disintegrants. Both materials have similar flowability but different particle size, facilitating the particle size assessment of the feeder performance. Paracetamol is a common API. It represents a poor flowability material and typical powder properties of APIs in this study.
P. Hou, M.O. Besenhard, G. Halbert, M. Naftaly, D. Markl, Development and implementation of a pneumatic micro-feeder for poorly-flowing solid pharmaceutical materials, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2023, 122691, ISSN 0378-5173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.122691.

