Electromagnetic drop-on-demand (DoD) technology as an innovative platform for amorphous solid dispersion production
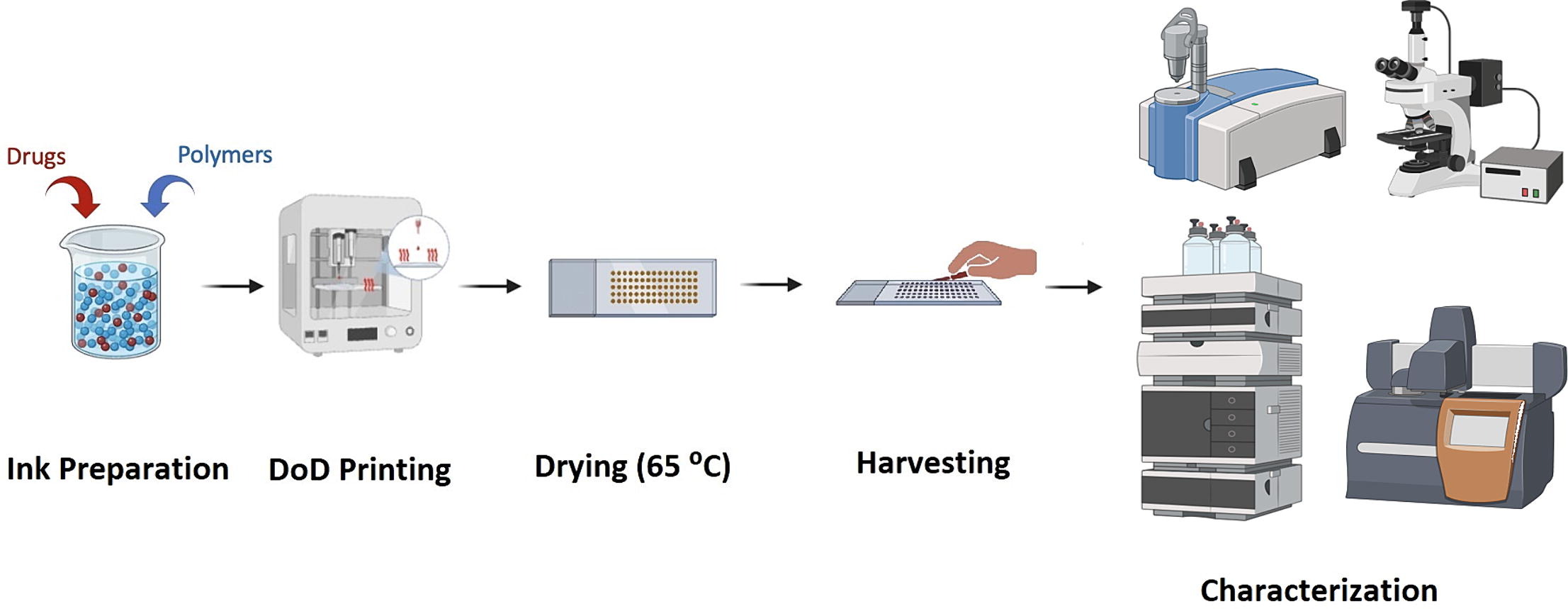
Production of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) is an invaluable technique to promote the solubility and bioavailability of medicinal substances. ASD is manufactured using a variety of classic and modern techniques, most of which rely on either melting or solvent evaporation. This proof-of-concept study is the first ever to introduce electromagnetic DoD as an alternative solvent evaporation-based method for producing ASD. 3D printing of ASDs for three drug-polymer combinations (efavirenz-Eudragit L100-55, lumefantrine-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate, and favipiravir-polyacrylic acid) was investigated to ascertain the reliability of this technique.
Polarized light microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction, and Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy results all supported the 3D printing of ASD for the three drugs, which significantly increases the equilibrium solubility of efavirenz from 0.03 ± 0.04 µg/ml to 21.18 ± 4.20 µg/ml, and the equilibrium solubility of lumefantrine form 1.26 ± 1.60 µg/ml to 20.21 ± 6.91 µg/ml. Overall, the study’s findings show how this new electromagnetic DoD technology has the potential to become a cutting-edge 3D printing solvent-evaporation technique for the continuous manufacturing of ASDs for a variety of drugs.
Read more here
Materials
Efavirenz and lumefantrine were provided by TCI America (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Portland, Oregon, USA). Favipiravir was provided by Hangzhou Longshine Biotech Co., Ltd. (Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, China). AquaSolve™ HPMC-AS MG (Mw. 103,200 g/mol) was provided by Ashland™ (Wilmington, Delaware, United States). Eudragit L100-55 (Mw. 250,000 g/mol) was purchased from Evonik Nutrition & Care GmbH (Kirschenalle, Darmstadt, Germany).
Abdelrahman M. Helmy, Anqi Lu, Ishaan Duggal, Kristina P. Rodrigues, Mohammed Maniruzzaman,
Electromagnetic drop-on-demand (DoD) technology as an innovative platform for amorphous solid dispersion production, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2024, 124185, ISSN 0378-5173, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124185.
Read also our introduction article on 3D Printing here:


