A self-emulsifying Omega-3 ethyl ester formulation (AquaCelle) significantly improves eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid bioavailability in healthy adults
Purpose
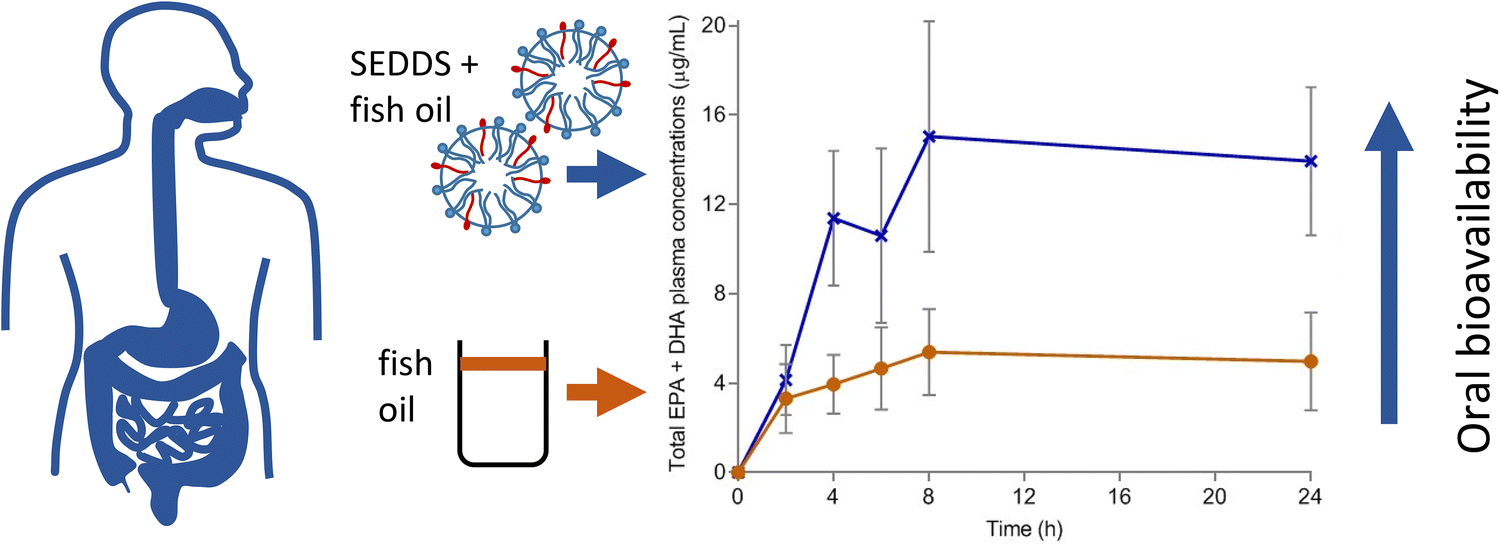
Application of intelligent formulation design has the ability to address the poor bioavailability and improve the fasted state bioavailability of fish oils. In this study we assessed the ability of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS), AquaCelle®, as an additive to enhance the oral absorption of Omega-3 ethyl esters (EE) in healthy subjects under low-fat diet conditions.
Methods
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) EE were formulated with AquaCelle®. A single dose (680 mg dose of oil containing 272 mg of EPA EE and 204 mg of DHA EE), randomized, double-blind, study measured uptake of EPA and DHA over 24 h in healthy adults. Participants were randomized into two groups, receiving either the SEDDS AquaCelle® fish oil formulation or the unformulated fish oil EE as control.
Results
The AquaCelle® fish oil EE formulation demonstrated instant and complete emulsification on addition to water to produce an emulsion with an average diameter of 43 μm, compared to the oil alone which did not emulsify. The study revealed a significant difference in absorption (Cmax and AUC0–24h) between the AquaCelle® group and the control group. The AquaCelle® group was capable of increasing maximum plasma concentrations and absorption (AUC0–24h) of total Omega-3 (EPA + DHA) 3.7- and 7.1-fold, respectively, compared to the control.
Conclusion
Formulating Omega-3 EE with a SEDSS concentrate (AquaCelle®) demonstrated a significant improvement in the oral absorption of Omega-3 fatty acids without requiring a high-fat meal.
Article Information:


