Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) for Tablet Coating Applications: Enhancing Formulation Flexibility
Purpose: Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is a well-established polymer for film coating. PVA is a synthetic, bio-compatible and toxicologically well characterized polymer. It is frequently used in pre-mixed coating formulations. Fixed combinations with additional ingredients are well established. By individual formulation development the performance of the coating can be further optimized. Properties of the polymeric films can be influenced and finetuned according to targeted requirements. However, techniques for the characterization of film coated tablets are quite limited. Frequently only visual inspections are performed. Therefore, it is of interest to develop a reliable characterization technique of coated tablets that can easily be implemented in early formulation development.
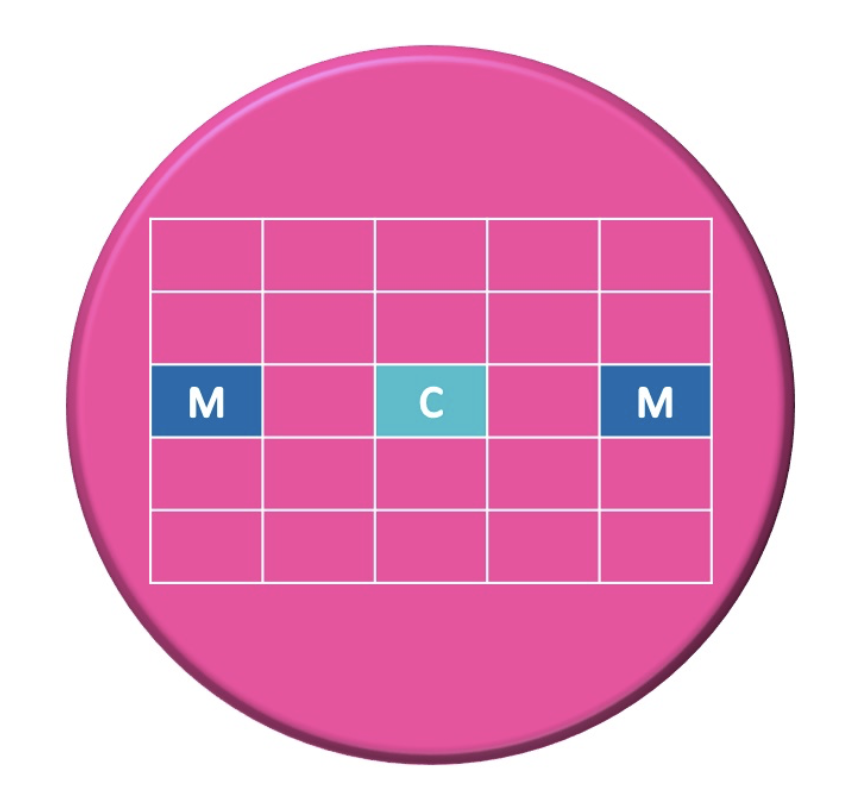
Methods: Tablet cores were manufactured using a rotary tablet press (Korsch PH230/14) at 76Upm; compression force: 20kN; height: 5 mm; tablet diameter: 11 mm; targeted tablet weight: 500 mg. A simplified core formulation was used: 98,5% mannitol + 1,5% magnesium stearate. Coating was performed using a rotating drum coater type LDCS from Vector Freund Corporation. Different plasticizers were compared at 10% and 30%: Triethyl citrate, glycerol, triacetin and different sugar alcohols: Sorbitol and mannitol. Targeted weight gain was set to 3%. Roughness of the tablets depends on the selected measurement region. It is expected that the greater the distance to the center of the tablet is the greater will be the roughness. The measurement regions for characterizing the roughness close to the border of the tablet must be well defined. A dedicated laser scanning microscopy method (LSM) was established to evaluate the surface structure of the various film coatings using a Keyence VK-X210 laser microscope. A defined raster was established to provide reliable information on the tablet surface and to evaluate the surface roughness at defined regions (central and marginal regions). A schematic view of the surface areas is presented in Figure 1.
Results: Analytical results of the tablet surface roughness are presented in Figure 2 & Figure 3. For the evaluated formulations the surface roughness is mostly independent of the measurement region. Especially triethyl citrate, triacetin and mannitol show a positive impact on the reduction of coating surface roughness. The addition of sorbitol also shows positive effects on the tablet surface. At higher concentrations (30%) the finishing of the tablets can even be further improved. For glycerol independent from the applied concentration nearly no changes in surface roughness could be observed.
Conclusion: Different plasticizers were successfully evaluated in combination with PVA. The established LSM method provides an important tool for formulation development and enables a thorough characterization and understanding of the film surface. In addition to common plasticizers like triethyl citrate or triacetin the use of mannitol and sorbitol can be highly interesting to improve the surface finishing of PVA based coatings. 2019 AAPS PharmSci 360
Join: Coating with Polyvinyl Alcohol: When Coating Runs Smoothly to hear more!

