Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets – An Alternative to Spray Drying?
Spray drying is one of the most frequently used solvent-based processes for manufacturing amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs). However, the resulting fine powders usually require further downstream processing when intended for solid oral dosage forms. In this study, we compare properties and performance of spray-dried ASDs with ASDs coated onto neutral starter pellets in mini-scale. We successfully prepared binary ASDs with a drug load of 20% Ketoconazole (KCZ) or Loratadine (LRD) as weakly basic model drugs and hydroxypropyl-methyl-cellulose acetate succinate or methacrylic acid ethacrylate copolymer as pH-dependent soluble polymers. All KCZ/ and LRD/polymer mixtures formed single-phased ASDs, as indicated by differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction and infrared spectroscopy.
All ASDs showed physical stability for 6 months at 25 °C/65% rH and 40 °C/0% rH. Normalized to their initial surface area available to the dissolution medium, all ASDs showed a linear relationship of surface area and solubility enhancement, both in terms of supersaturation of solubility and initial dissolution rate, regardless of the manufacturing process. With similar performance and stability, processing of ASD pellets showed the advantages of a superior yield (>98%), ready to use for subsequent processing into multiple unit pellet systems. Therefore, ASD-layered pellets are an attractive alternative in ASD-formulation, especially in early formulation development at limited availability of drug substance.
Download the full articel as PDF here Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets—An Alternative to Spray Drying
or read it here
Materials
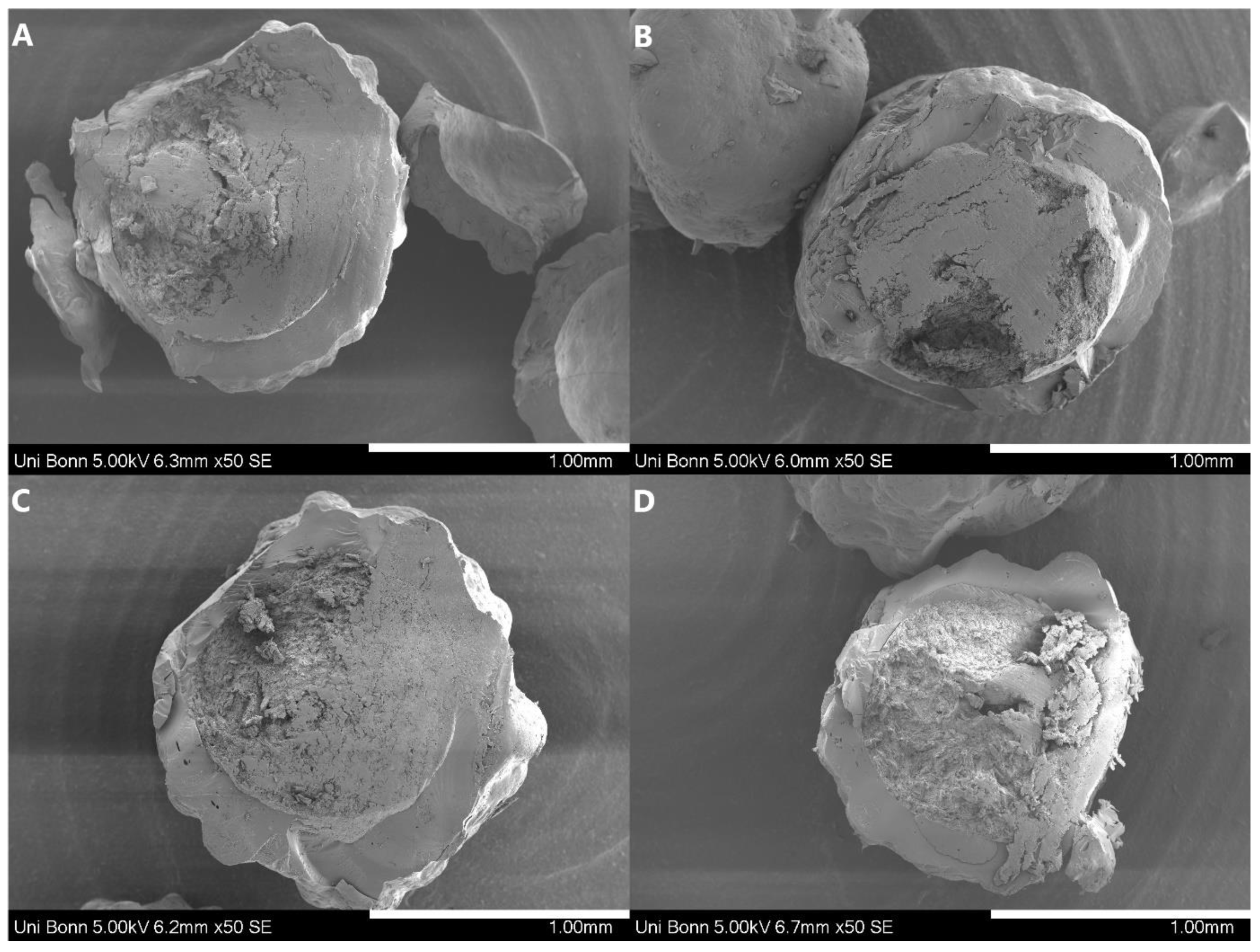
The model drugs ketoconazole (KCZ) and loratadine (LRD) were purchased from Sris Pharmaceuticals (Hyderabad, India). HPMCAS LG (hydroxypropyl-methylcellulose acetate succinate, wt%: methoxyl 20–24%, hydroxypropyl 5–9%, succinyl 14–18%; Mw = 18,000, HPMC-AS) was donated from Shin-Etsu Chemical (Tokyo, Japan). Eudragit L100-55 (methacrylic acid ethylacrylate copolymer, ratio 1:1, Mw = 320,000, EL100-55) was donated by Evonik (Darmstadt, Germany). Cellets 1000 (microcrystalline cellulose starter pellets, 1000–1400 µm) were provided by Glatt Pharmaceutical Services (Binzen, Germany).
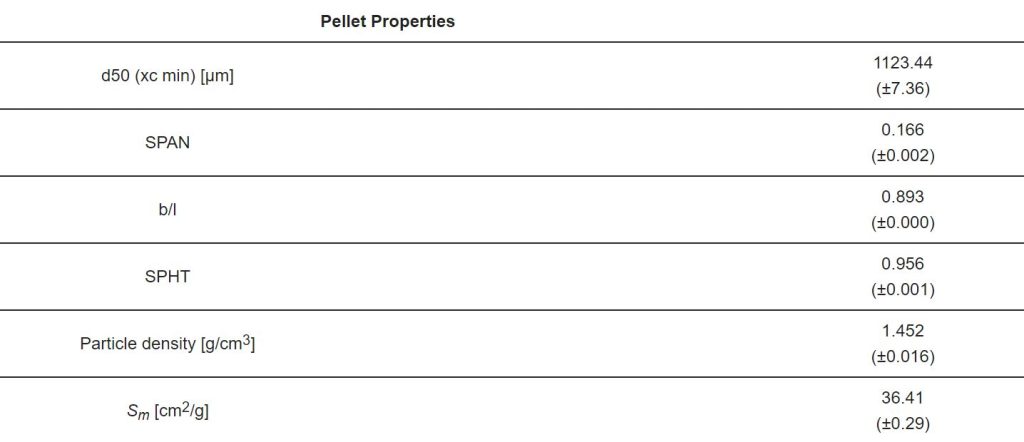
A detailed list of the pellets’ characteristics is shown in Table 1. Ethanol 96% (v/v) (technical grade) used in the sample preparation, and methanol (analytical grade) used for the HPLC analytics as well as the buffer salts disodium mono-hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate (Na2HPO4·12H2O) and monosodium dihydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate (NaH2PO4·12H2O) were obtained from VWR Chemicals GmbH (Darmstadt, Germany).
Neuwirth, M.; Kappes, S.K.; Hartig, M.U.; Wagner, K.G. Amorphous Solid Dispersions Layered onto Pellets—An Alternative to Spray Drying? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030764

