The Development of Innovative Dosage Forms of the Fixed-Dose Combination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
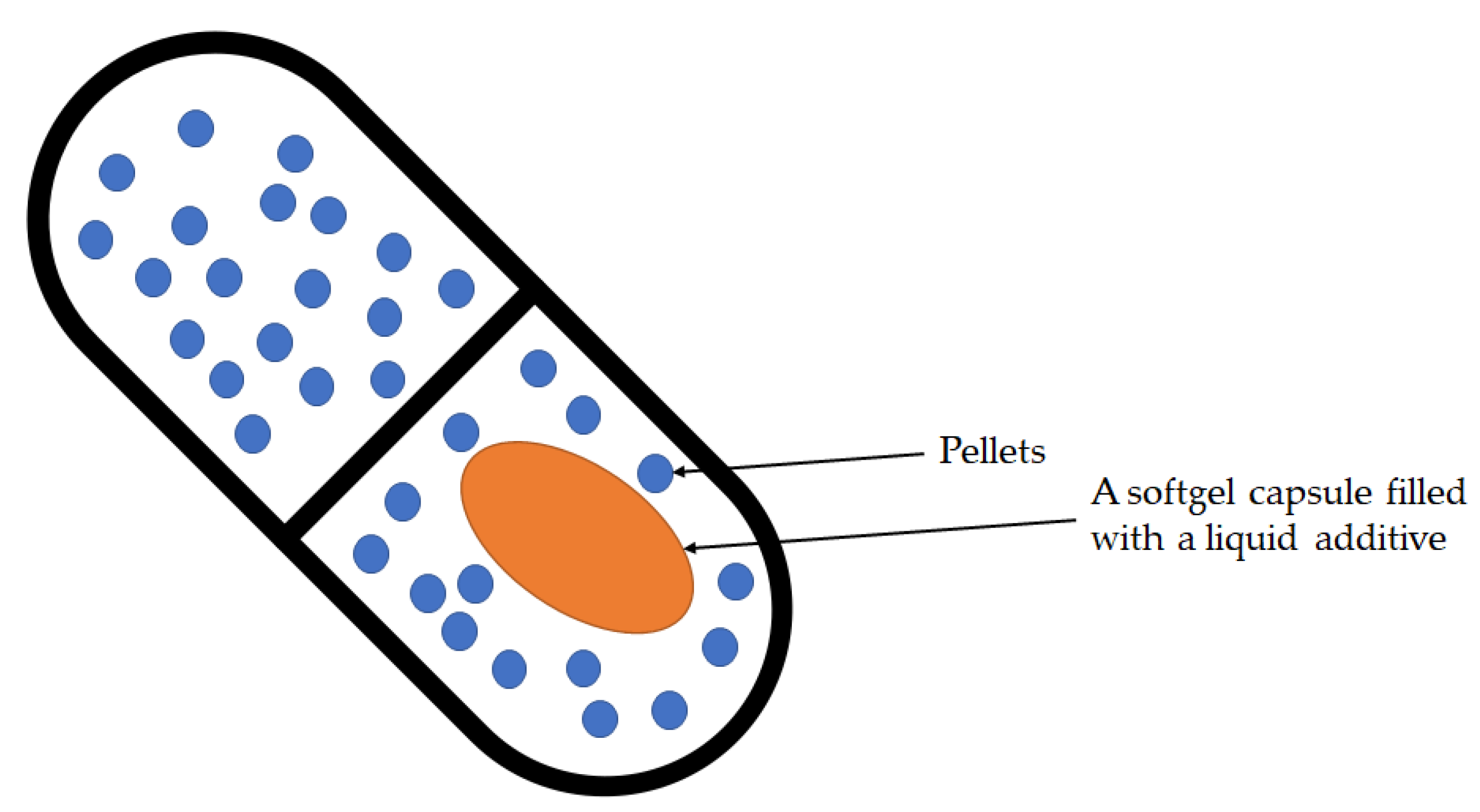
The development of innovative forms of combination drugs is closely related to the invention of the multilayer tablet press, polymers for pharmaceutical applications, the hot-melt extrusion process, and 3D printing in the pharmaceutical industry. However, combining multiple drugs within the same dosage form can bring many physicochemical and pharmacodynamic interactions. More and more new forms of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) have been developed due to work to overcome the incompatibility of active substances or to obtain different drug release profiles in the same dosage form. This review provides discussions of the application of various innovation formulation technologies of FDC drugs such as bilayer system, multilayer tablet, active film coating, hot-melt extrusion, and 3D printing, taking into account the characteristics of the key ingredients in the FDC formulation and presenting technological problems and challenges related to the development of combination drugs. Moreover, the article summarizes the range of dosage forms that have been made using these technologies over the past 30 years.
Continue reading here
About this article: Janczura, M.; Sip, S.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. The Development of Innovative Dosage Forms of the Fixed-Dose Combination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040834
Conclusions
Progress in applied pharmacy resulted in the spread of more complex drugs, which made it possible to improve the already existing medicinal products due to their innovation. It also initiated the use of compounds that could not be introduced into medicine earlier due to their biological and physicochemical properties. The development of oral dosage forms providing long and sustained release of the API (days or weeks) could transform care, significantly decrease patient burden in chronic disease management, and improve the effectiveness of therapy. Monolithic, multiple-layer, and multiarticulate systems are the most common type of FDCs. Currently, the leading manufacturing techniques utilized in industrial pharmaceutical companies rely on combined wet and dry granulation, hot-melt extrusion coupled with spray coating, and compression of bilayered tablets. Even though 3DP was introduced in the 1980s, there is still much research, especially in creating materials suitable for pharmaceutical and medical applications. Extrusion based on 3D printing is the technology most used to fabricate polypills and customize the dose, dosage form, and release the kinetics, potentially reducing the risk of patient non-compliance. Nowadays, personalized medicines are gaining importance in clinical settings, and 3D printing is highlighted in manufacturing complex and personalized 3D solid dosage forms that could not be manufactured using conventional techniques. One of the latest trends in 3DP is the use of versatile materials that can change their properties under the influence of external factors or over time. Structural modification over time, otherwise known as the fourth dimension, has created a new term known as “4D printing”.

