Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems: a promising noninvasive approach to bioavailability enhancement. Part II: formulation considerations
Abstract
Introduction
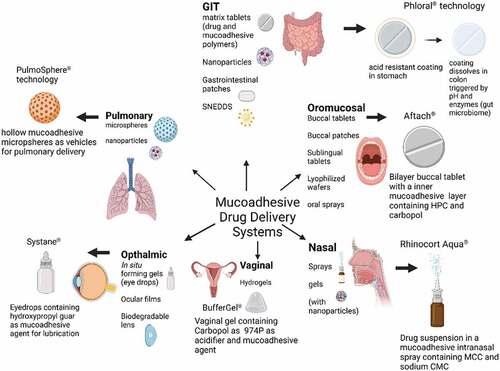
Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems (MDDS) are specifically designed to interact and bind to the mucosal layer of the epithelium for localized, prolonged, and/or targeted drug delivery. Over the past 4 decades, several dosage forms have been developed for localized as well as systemic drug delivery at different anatomical sites.
Areas covered
The objective of this review is to provide a detailed understanding of the different aspects of MDDS. Part II describes the origin and evolution of MDDS, followed by a discussion of the properties of mucoadhesive polymers. Finally, a synopsis of the different commercial aspects of MDDS, recent advances in the development of MDDS for biologics and COVID-19 as well as future perspectives are provided.
Highlights
Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems (MDDS) are designed to adhere to specific mucosal tissue sites (such as GIT, nasal, oral, pulmonary, vaginal ophthalmic, and intravesical) in the body for local or systemic action. Diverse applications of MDDS have emerged in the past few decades, which have been detailed in the manuscript.
Mucoadhesive polymers must have optimum moisture and surface energy to ensure proper wetting, swelling, and interpenetration into the mucus layer.
Chitosan is a cationic polymer with excellent mucoadhesive properties explored in MDDS via different routes. It binds to mucin via hydrogen and ionic bonds.
The degree of crosslinking, hydration, pH (charge on polymer), functional group, and molecular weight of the polymers dictates its mucoadhesive strength.
Thiolated polymers bind to the mucin via disulfide bonds and have an exceptional binding affinity to the mucus layer, making them desirable polymer candidates for numerous drug delivery applications.
Several recent MDDS demonstrate a combination of mucoadhesive polymers with other excipients such as permeation enhancers and hydrogels for versatile applications such as prolonged/controlled drug release or for improved drug absorption. These strategies are especially useful in the case of complications such as COVID-19.
Advancement in nanotechnology has diversified MDDS applications even further. The confluence of unique size and surface morphology of nano systems with mucoadhesive polymers have improved mucoadhesion along with increased cellular uptake and drug absorption.
Read more on Chitosan as a pharmaceutical excipient here:


