Role of Surfactant Micellization for Enhanced Dissolution of Poorly Water-Soluble Cilostazol Using Poloxamer 407-Based Solid Dispersion via the Anti-Solvent Method
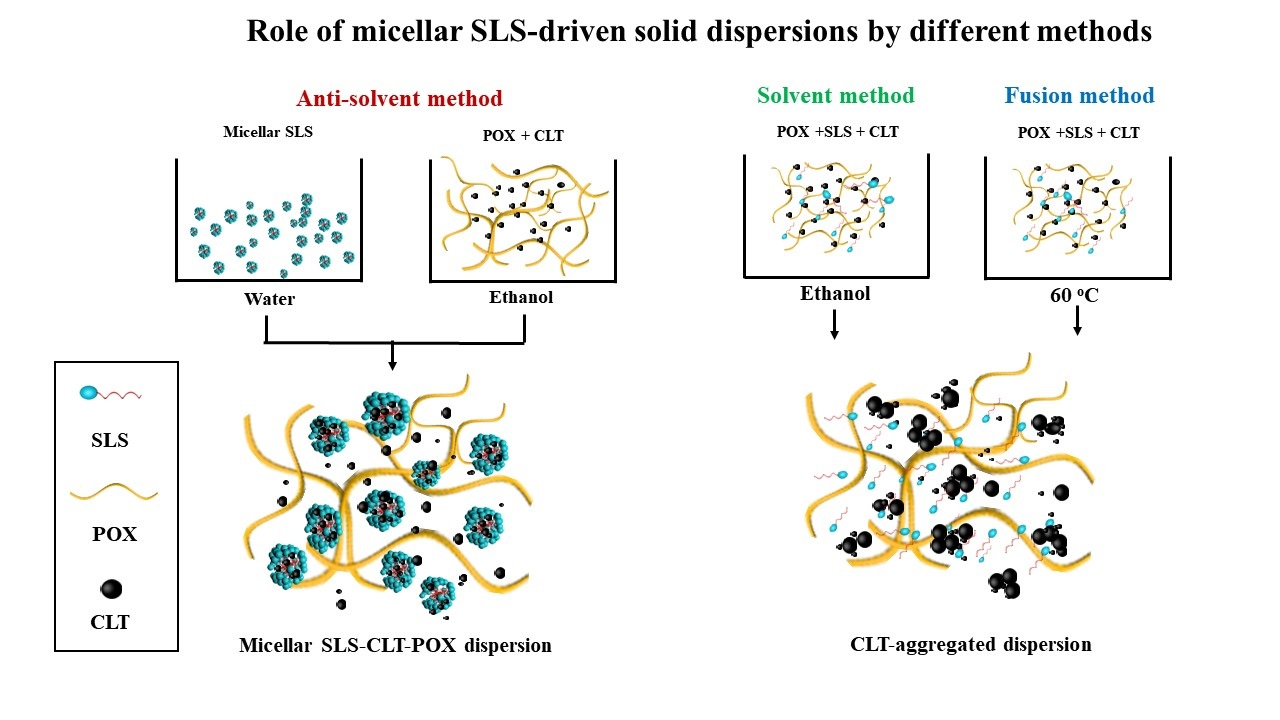
This study aimed to investigate the role of micellization of sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) in poloxamer 407 (POX)-based solid dispersions (POX-based SDs) using the anti-solvent method in enhancing the dissolution rate of practically water-insoluble cilostazol (CLT). Herein, SLS was incorporated into CLT-loaded SDs, at a weight ratio of 50:50:10 of CLT, POX, and SLS by three different methods: anti-solvent, fusion (60 °C), and solvent (ethanol) evaporation. The SDs containing micellar SLS in the anti-solvent method were superior in the transformation of the crystalline form of the drug into a partial amorphous state.
It was notable that there was an existence of a hydrophobic interaction between the surfactant and the hydrophobic regions of polymer chain via non-covalent bonding and the adsorption of micellar SLS to the POX-based SDs matrix. Moreover, SLS micellization via the anti-solvent method was effectively interleaved in SDs and adhered by the dissolved CLT, which precluded drug particles from aggregation and recrystallization, resulting in improved SD wettability (lower contact angle) and reduced particle size and dissolution rate.
In contrast, SDs without micellar SLS prepared by the solvent method exerted drug recrystallization and an increase of particle size, resulting in decreased dissolution. Incorporation of surfactant below or above critical micellar concentration (CMC) in SDs using the anti-solvent method should be considered in advance. Dissolution results showed that the pre-added incorporation of micellar SLS into POX-based SDs using the anti-solvent method could provide a way of a solubilization mechanism to enhance the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs.
Download the full article as a PDF here or read it here
Materials: CLT was obtained from Chemagis Co. Ltd. (Ramat Hovav, Israel). SLS was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint-Louis, MO, USA). Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC.6 cps) was obtained through the courtesy of Richwood Co. (Seoul, Korea). Poloxamer 407, polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 (PVP K30), D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS), and soluplus were supplied by BASF Chemicals (Ludwigshafen, Germany). Polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG 6000) was obtained from Yakuri Pure Chemicals (Tokyo, Japan). All the other chemicals were of analytical grade and were used without further purification.
Article information: Jin, G.; Ngo, H.V.; Cui, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-J. Role of Surfactant Micellization for Enhanced Dissolution of Poorly Water-Soluble Cilostazol Using Poloxamer 407-Based Solid Dispersion via the Anti-Solvent Method. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050662

