Mucoadhesive bilayered buccal platform for antifungal drug delivery into the oral cavity
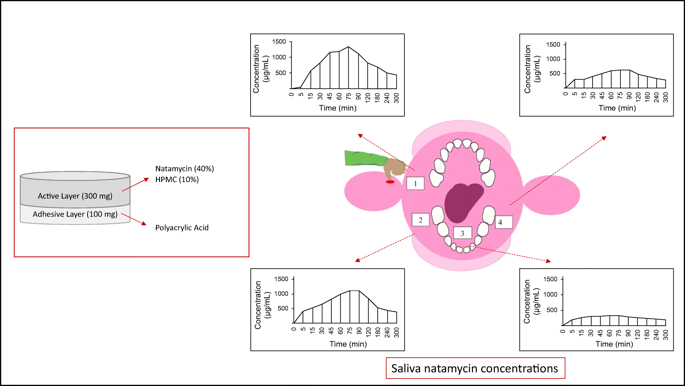
A drug delivery technology comprising a mucoadhesive bilayered buccally anchored tablet containing natamycin was developed. The concept was to anchor the tablet to the buccal tissue and allow controlled release of the drug through the matrix into the mouth. Carbomer (Carbopol ® 974 P NF) was used to formulate the mucoadhesive layer. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) (Methocel® K4M) at 10, 15, 20, and 40% w/w was used for the drug-containing layer. Natamycin, an amphoteric macrolide antifungal agent, was incorporated into the formulations. In addition, tablets containing erythrosine as a marker were prepared in order to examine the distribution and retention of the dye in the oral cavity.
As expected, the in vitro analysis showed that the concentration of natamycin released decreased with the increasing proportion of HPMC in the formulation. A small volunteer study was conducted using the tablets containing 10% and 20% HPMC to quantitate the patterns of distribution of the drug released into the oral cavity (upper right buccal vestibule, lower right and left buccal vestibules, and sublingual region). The mucoadhesive bilayered buccal tablet formulation provided a unidirectional release of the drug from the tablet into the oral cavity in a prolonged release fashion, maintaining drug concentration above the MIC value (2 μg/mL) for Candida albicans. The amount of the drug in the sublingual region was found to be lowest when compared with other regions, which is due to the higher flow of saliva in this region.
Continue on Mucoadhesive bilayered buccal platform for antifungal drug delivery into the oral cavity
Excipient Information
Carbopol® 974P NF Polymer
Suitable applications for Carbopol® 974P NF: Oral and topical
Residual solvent for Carbopol® 974P NF: Ethyl acetate
Carbopol® 974P NF polymer was introduced for use in oral and mucosal contact applications such as oral liquids, bioadhesive formulations, oral care formulations and extended release tablets. Additionally, Carbopol 974P NF polymer can be used to formulate viscous gels, emulsions and suspensions.
It is a highly crosslinked polymer and produces highly viscous gels with rheology similar to mayonnaise. Drug release from extended release tablets is affected by differences in the rates of hydration and swelling of the polymer hydrogel, which are largely defined by the crosslinker levels. Lightly crosslinked polymers, such as Carbopol 971P NF polymer, tend to be more efficient in controlling drug release than highly crosslinked polymers such as Carbopol 974P NF polymer. More Information
Methocel® K4M
METHOCEL™ cellulose ethers are water-soluble polymers derived from cellulose. The METHOCEL™ product range encompasses methylcellulose and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose) – each available in different grades to address a wide range of applications including tablet coatings, granulation, controlled release, drug layering, vegetarian hard-shell capsules and amorphous drug stabilization.
METHOCEL™ products have been in continuous production for more than 70 years with production facilities and deep product expertise located around the globe.
The METHOCEL™ Premium family of products offers exceptional flexibility and a broad range of properties typically not found in other water-soluble polymers. In many applications, two, three or even more ingredients may be needed to do the same job performed by one METHOCEL™ product. That means one ingredient can do the job of many, saving money and time.
Article information:
Uzunoğlu, B., Wilson, C.G., Sağıroğlu, M. et al. Mucoadhesive bilayered buccal platform for antifungal drug delivery into the oral cavity. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-020-00798-1

